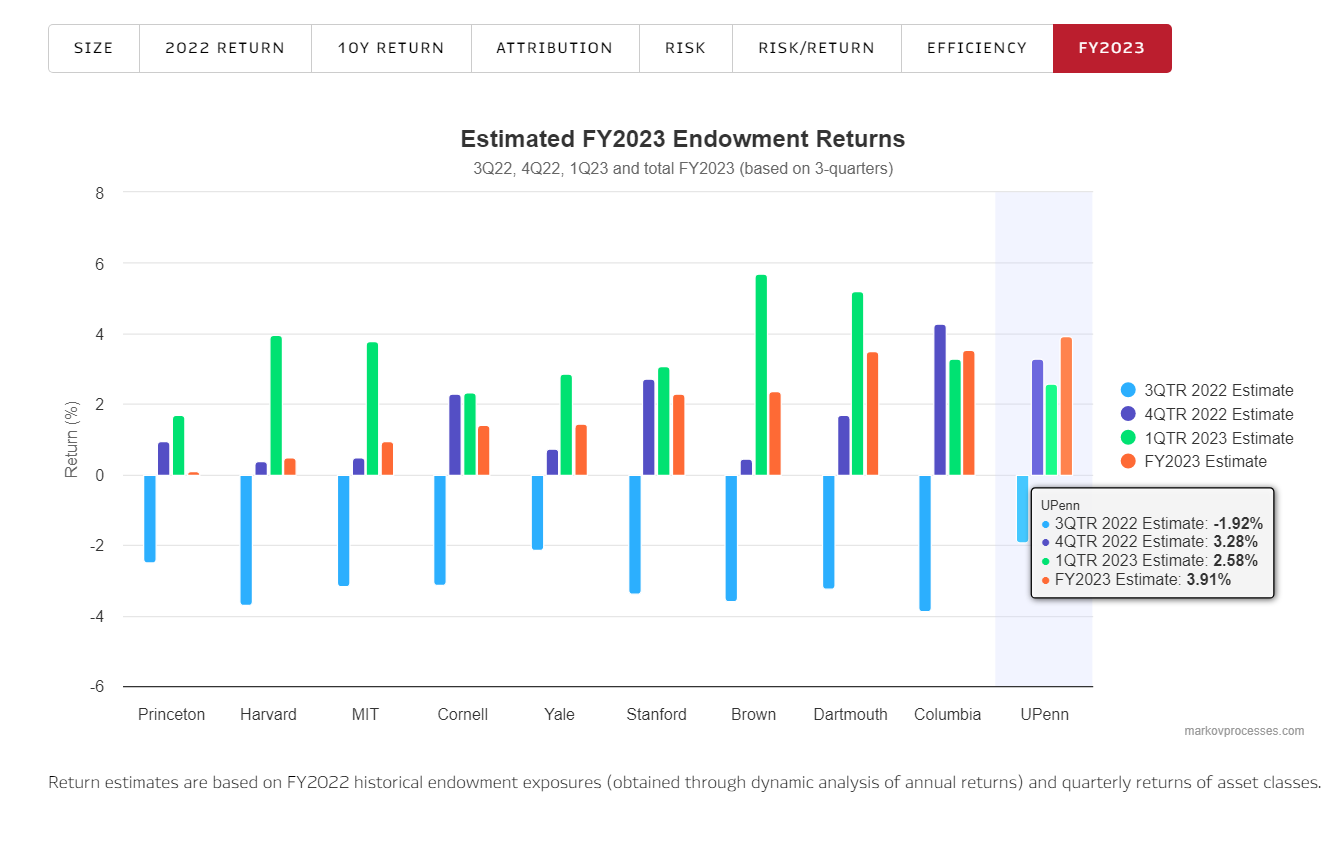
Endowments and pensions continue to post gains, but exposure to private markets pushes many below benchmarks

Endowments and pensions continue to post gains, but exposure to private markets pushes many below benchmarks
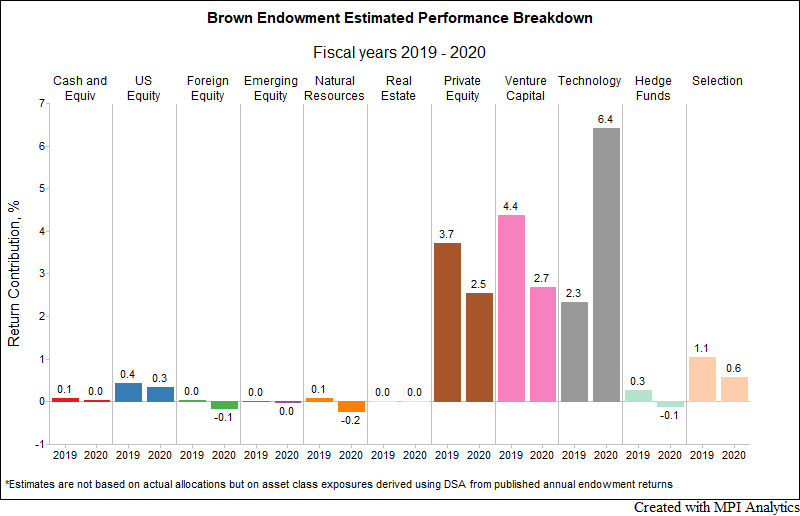
For the second straight year, Brown outperformed all other Ivy endowments by a large margin. Our research team, using MPI Stylus Pro to dissect the endowment annual returns, provides a plausible explanation of the endowment’s spectacular results.
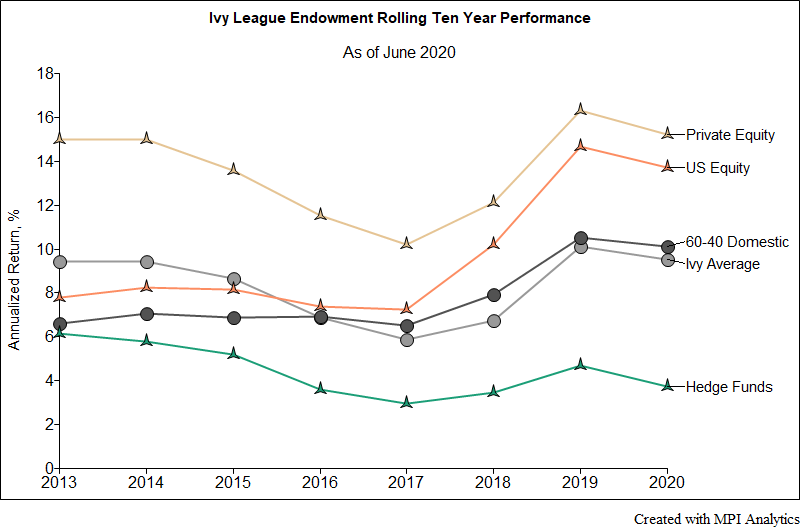
We take a quick look at Ivy schools’ endowments’ performance results both for the 2020 fiscal year and also long-term for 10-year periods.

“…how was it possible for so many endowments to make bad choices among private equity and venture capital funds? The following chart from Markov suggests that it is down to outlandishly wide variations in performance within the private equity/venture capital world,” writes John Authers about MPI’s research in his opinion piece on Bloomberg.
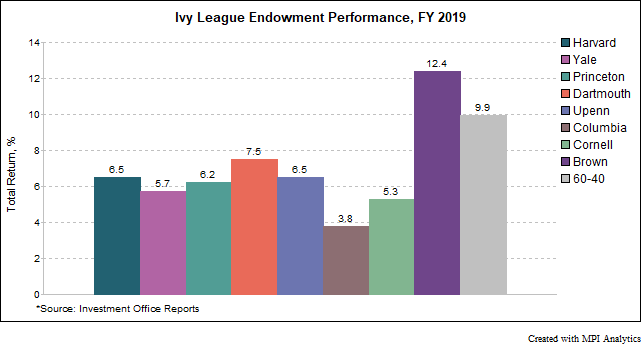
Fiscal year 2019 was a curious year for the Ivy League endowments. In a year with strong returns in key private market investment classes, the average Ivy underperformed a traditional domestic balanced 60-40 portfolio in FY 2019. Ivies also experienced a wider dispersion of returns and saw a shift in the historical positioning of performance leaders and laggards.
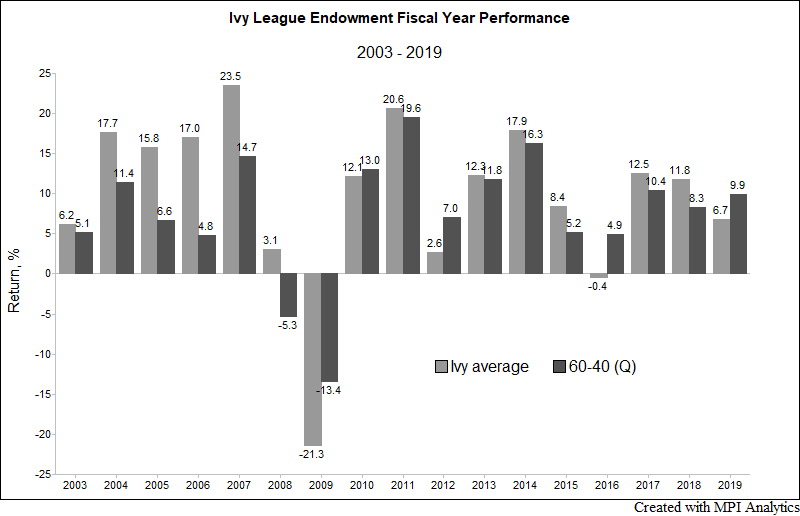
The grades for all the Ivy League endowments are in – and they are rather disappointing. Save for Brown, all Ivies underperformed the 9.9% return of a domestic 60-40 portfolio in fiscal year 2019. The Ivy average in FY 2019 was 6.7%, significantly underperforming the 60-40 and reversing two years in which they outperformed the traditional domestic benchmark.
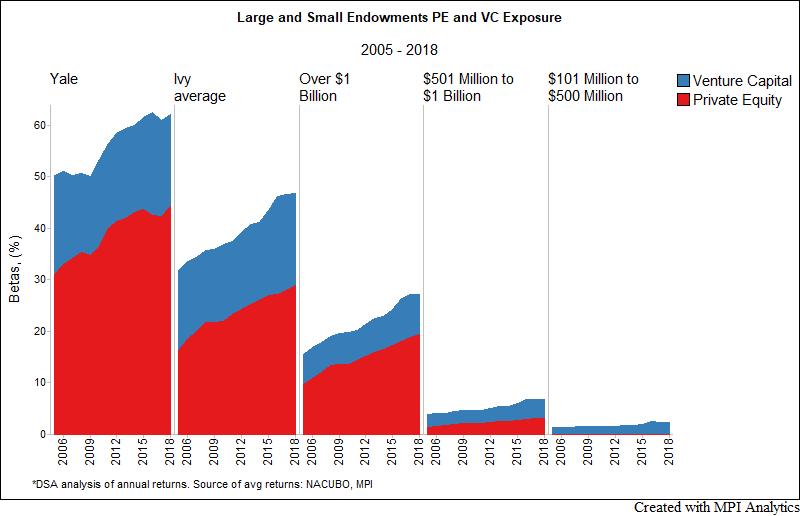
We sought to examine the relationships between endowment size, pedigree and exposure to private assets and what impact that may have on portfolio risk using advanced quantitative methods and a cutting edge methodology to better model the true behavior and risk profile of private market assets.
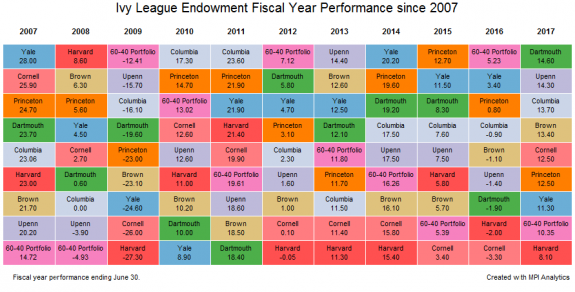
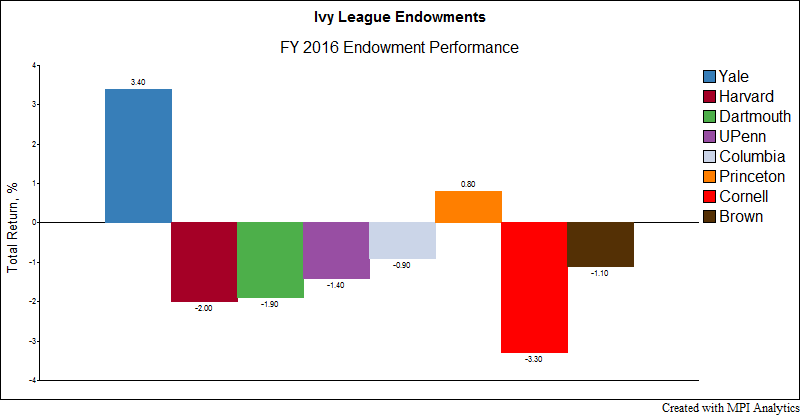
In stark contrast to FY 2016, this past year was a strong one for most endowments. In fact, nearly all the Ivy League endowments, Harvard being the only exception, beat the 60-40 portfolio, a commonly cited benchmark that endowments measure their performance against.
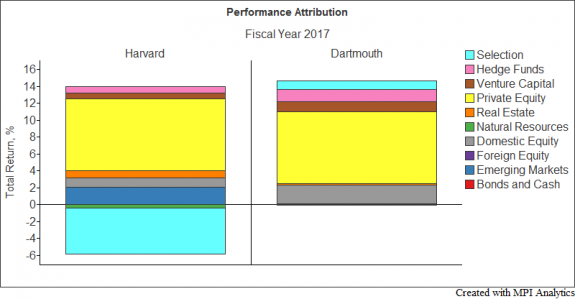
The returns of endowments can be attributed to two fundamental components: asset allocation and security selection. Asset allocation is what a factor model is generally able to explain, shown in terms of factor exposures.
An 1873 meeting that brought Harvard, Yale and Princeton together to codify the rules of American football also debuted a sports conference later known as the “Ivy League — eight elite institutions whose heritage, dating from pre-Revolutionary times, became formative influences shaping American character and culture. These schools also pioneered endowment investment management, thus helping to secure the nation’s educational legacy for posterity.